


...Om de verspreiding van antimicrobiële resistentie te voorkomen, moeten we het gebruik van antibiotica binnen de wondzorg aanzienlijk verminderen.
Hoewel de Wereldgezondheidsorganisatie (WHO) AMR aanpakt met een wereldwijd actieplan, is er nog veel ruimte om bij te dragen aan de preventie van AMR binnen wondverzorging.1
Strijden tegen AMR doen we samen door actie te ondernemen op elk niveau binnen wondzorg, van generalist tot expert.
De European Wound Management Association beveelt aan om het onnodig gebruik van antibiotica te vermijden d.m.v adequaat infectiepreventie/-management en geschikte hygiëneprotocollen.2
Met de merken Cutimed® en Leukoplast® biedt Essity een uitgebreid assortiment wondzorgproducten die infecties effectief bestrijden, zonder bekend risico dat ze verder bijdragen aan antimicrobiële resistentie.
Door bij iedere stap in wondverzorging de juiste middelen voor infectiemanagement te kiezen kan het onnodig gebruik van antibiotica worden vermeden:

Met de merken Cutimed® en Leukomed® biedt Essity een uitgebreid assortiment wondzorgproducten die het onnodig gebruik van antibiotica kunnen helpen vermijden.
Antibiotica doden bacteriën of remmen hun groei. Als een antibioticum regelmatig tegen een bacterie wordt gebruikt, kan de bacterie resistent worden.
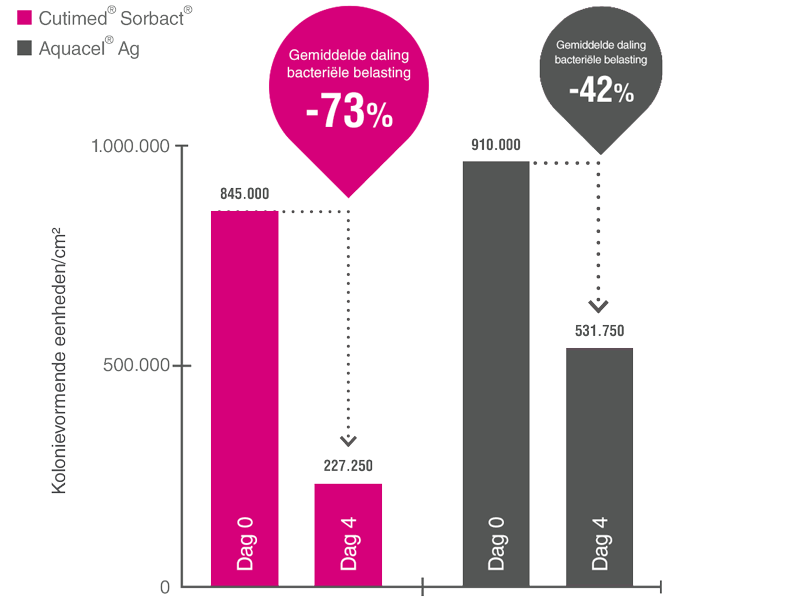
Bij lokaal infectiemanagement maakt de Sorbact®-technologie hier het verschil: er is geen opbouw van resistentiemechanisme bekend!
De Sorbact®-technologie doodt de bacteriën niet, maar bindt puur natuurkundig bacteriën (en schimmels) veilig aan zich. Deze technologie verwijdert bacteriën zonder het vrijkomen van antibacterieel werkende stoffen.3
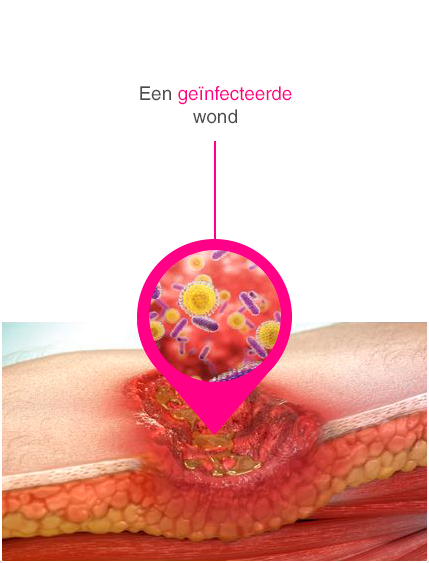
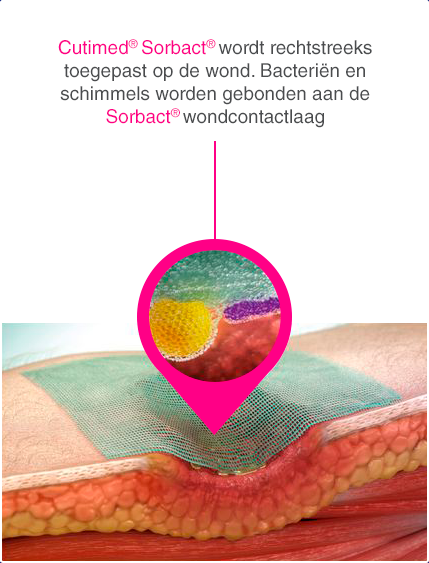
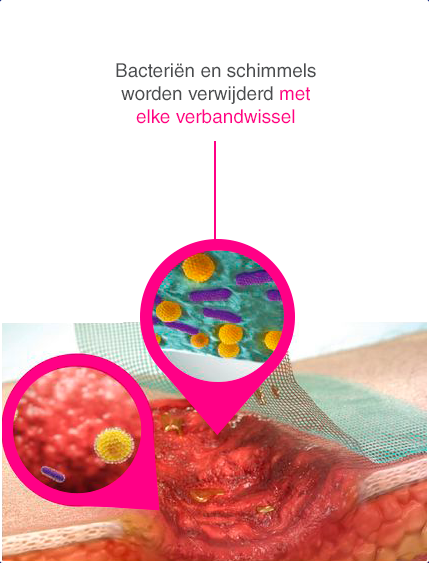
Cutimed® Sorbact® biedt een compleet assortiment voor lokaal infectiemanagement bij acute, secundair en complex genezende wonden en kan voor langere tijd ingezet worden totdat de infectie is bestreden. Dit biedt vele voordelen die jouw dagelijkse werk makkelijker maken.
Daarnaast kan Cutimed® Sorbact® ook preventief worden ingezet ter voorkoming van wondinfecties.



De innovatieve en efficiënte debridement pad

(Lokaal) Infectiemanagement gebaseerd op een puur natuurkundig werkingsmechanisme

Transparant wondverband voor een effectieve beheersing van infectierisico
Essity Netherlands B.V.
Arnhemse Bovenweg 120
3708 AH Zeist
Tel: 030-6984700
medical.cs.nl@essity.com